Association of Biologic Therapy with Coronary Inflammation in Patients with Psoriasis as assessed by Perivascular Fat Attenuation Index | Elnabawi et al.

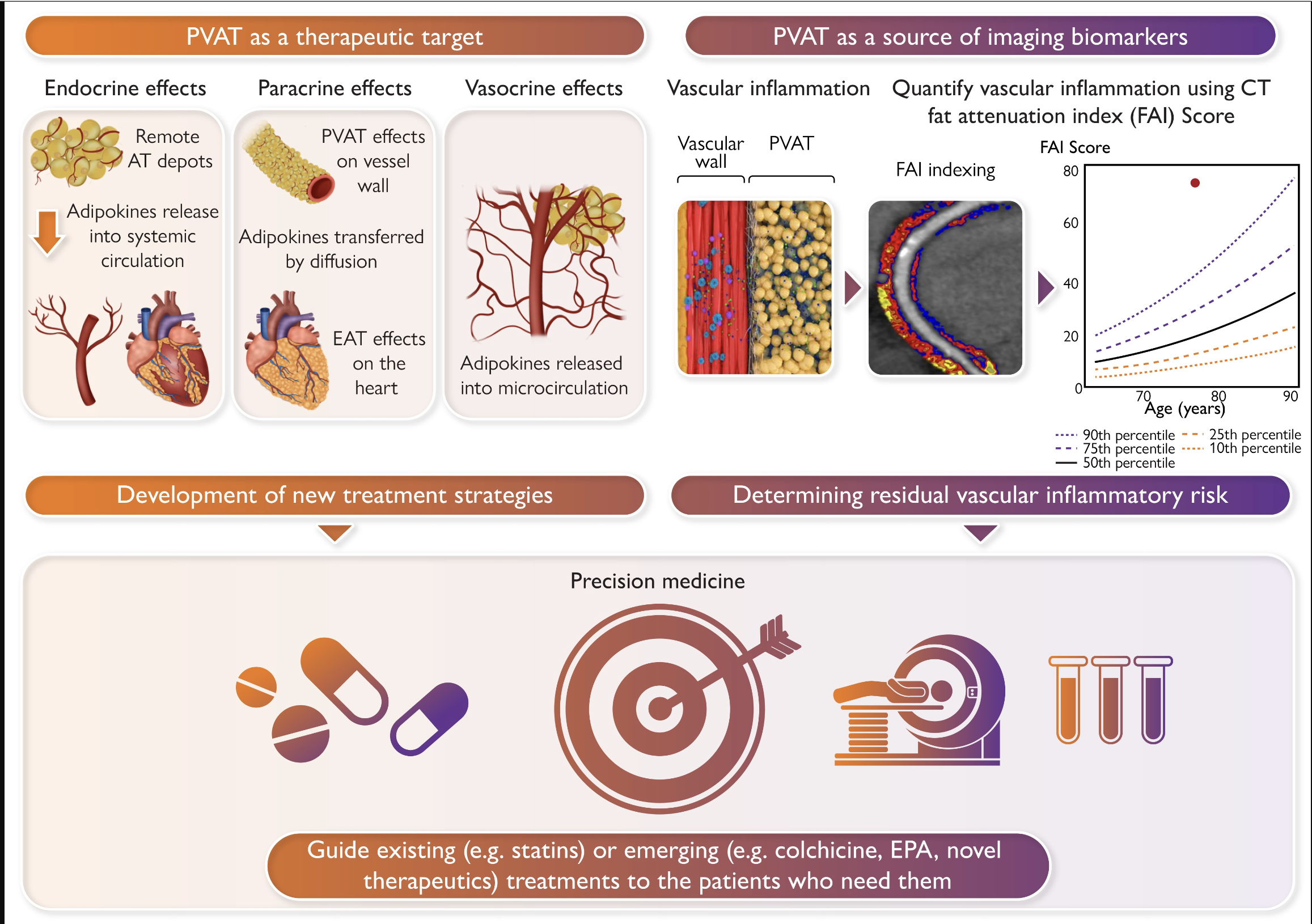
Chronic inflammatory diseases, including psoriasis, are associated with increased cardiovascular (CV) risk, which may be reduced when treating the underlying psoriasis.
This finding has opened interest to whether treating areas of low-grade inflammation in the body may be associated with downstream CV risk. A study of patients with moderate to severe psoriasis recently found that treatment of psoriasis with biologic therapy, including anti–tumor necrosis factor α (TNF-α), anti–interleukin (IL) 17, or anti–IL-12/23 therapy, may modulate coronary plaque compared with no biologic therapy.