Atherosclerosis affecting fat: What can we Learn by Imaging Perivascular Adipose Tissue?
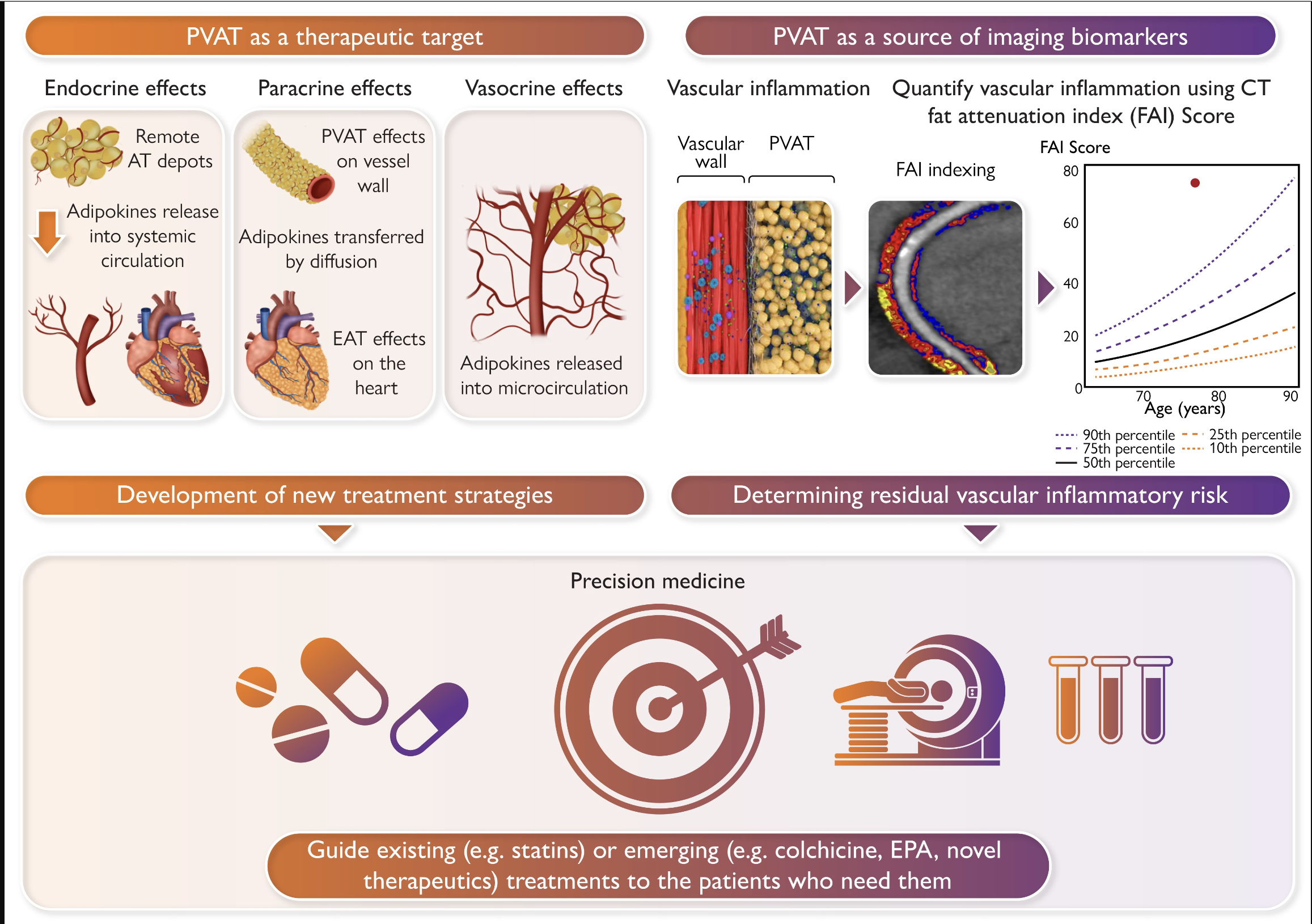
Perivascular adipose tissue (PVAT) surrounding the human coronary arteries, secretes a wide range of adipocytokines affecting the biology of the adjacent vascular wall in a paracrine way. However, we have recently found that PVAT also behaves as a sensor of signals coming from the vascular wall, to which it reacts by changing its morphology and secretory profile.
Indeed, vascular inflammation, a key feature of vascular disease pathogenesis, leads to the release of inflammatory signals that disseminate into local fat, inducing local lipolysis and inhibiting adipogenesis. This ability of PVAT to sense inflammatory signals from the vascular wall, can be used as a “thermometer” of the vascular wall, allowing for non-invasive detection of coronary inflammation. Vascular inflammation induces a shift of PVAT’s composition from lipid to aqueous phase, resulting into increased computed tomography (CT) attenuation around the inflamed artery, forming a gradient with increasing attenuation closer to the inflamed coronary artery wall.
These spatial changes in PVAT’s attenuation are easily detected around culprit lesions during acute coronary syndromes. A new biomarker designed to captured these spatial changes in PVAT’s attenuation around the human coronary arteries, the Fat Attenuation Index (FAI), has additional predictive value in stable patients for cardiac mortality and non-fatal heart attacks, above the prediction provided by the current state of the art that includes risk factors, calcium score and presence of high risk plaque features. The use of perivascular FAI in clinical practice may change the way we interpret cardiovascular CT angiography, as it is applicable to any coronary CT angiogram, and it offers dynamic information about the inflammatory burden of the coronary arteries, providing potential guidance for preventive measures and invasive treatments.