A Novel machine Learning-Derived Radiotranscriptomic Signature of Perivascular Fat improves Cardiac Risk Prediction using Coronary CT Angiography

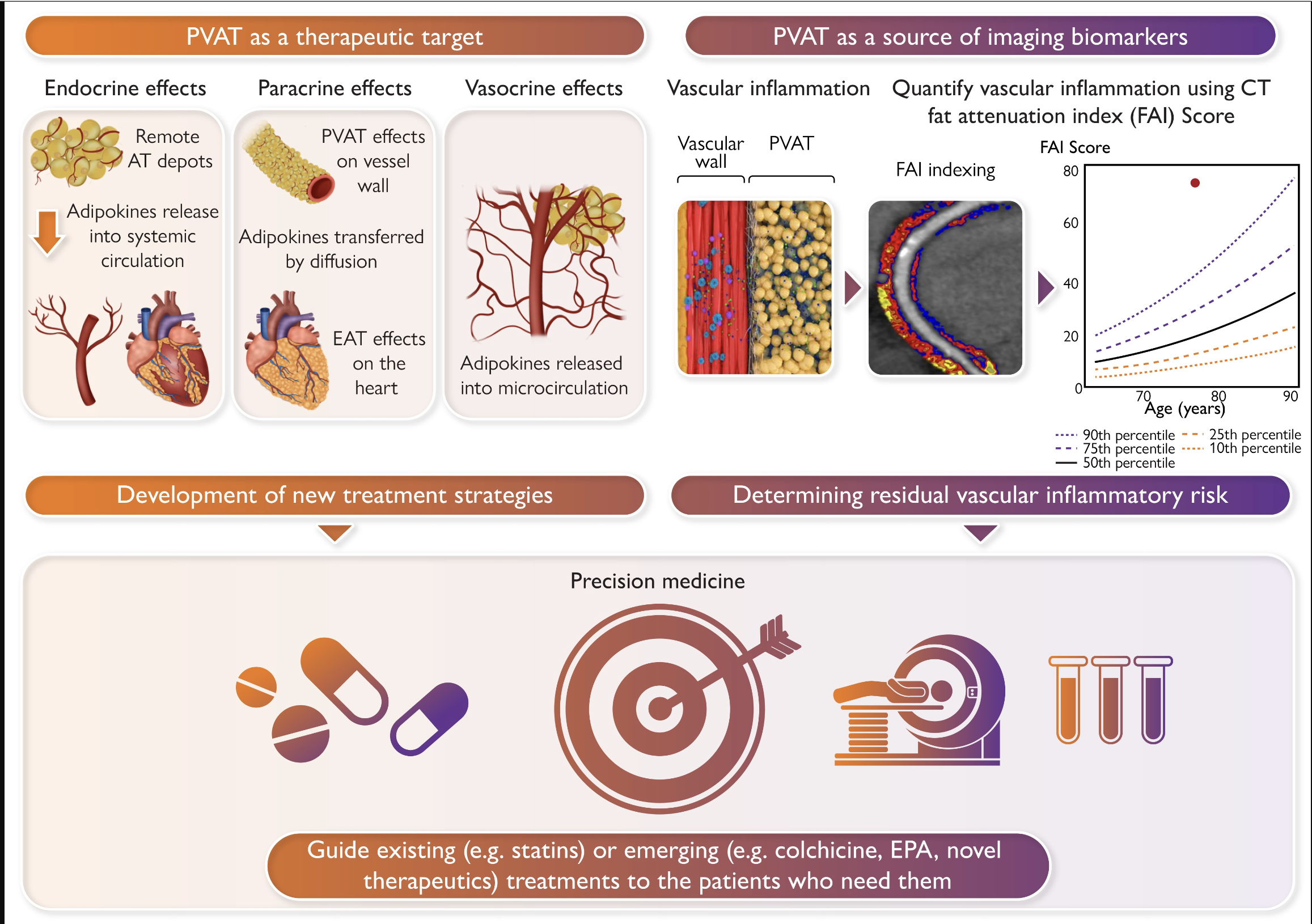
Coronary inflammation induces dynamic changes in the balance between water and lipid content in perivascular adipose tissue (PVAT), as captured by perivascular Fat Attenuation Index (FAI) in standard coronary CT angiography (CCTA). However, inflammation is not the only process involved in atherogenesis and we hypothesised that additional radiomic signatures of adverse fibrotic and microvascular PVAT remodelling, may further improve cardiac risk prediction.
We present a new artificial intelligence-powered method to predict cardiac risk by analysing the radiomic profile of coronary PVAT, developed and validated in patient cohorts acquired in three different studies.